Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Ir 2109
Caricato da
Chavi AlmeidaDescrizione originale:
Titolo originale
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Ir 2109
Caricato da
Chavi AlmeidaCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Data Sheet No.
PD60163-U
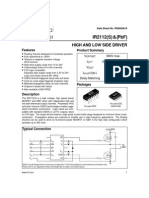
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Features
HALF-BRIDGE DRIVER
Product Summary
VOFFSET IO+/VOUT ton/off (typ.) Dead Time 600V max. 120 mA / 250 mA 10 - 20V 750 & 200 ns 540 ns
Floating channel designed for bootstrap operation
Fully operational to +600V Tolerant to negative transient voltage dV/dt immune Gate drive supply range from 10 to 20V Undervoltage lockout for both channels 3.3V, 5V and 15V input logic compatible Cross-conduction prevention logic Matched propagation delay for both channels High side output in phase with IN input Logic and power ground +/- 5V offset. Internal 540ns dead-time, and programmable up to 5us with one external RDT resistor (IR21094) Lower di/dt gate driver for better noise immunity Shut down input turns off both channels. Available in Lead-Free
(programmable up to 5uS for IR21094)
Packages
14 Lead SOIC
Description
The IR2109(4)(S) are high voltage, high speed power 8 Lead SOIC MOSFET and IGBT drivers with dependent high and 14 Lead PDIP low side referenced output channels. Proprietary HVIC and latch immune CMOS technologies enable ruggedized monolithic construction. The logic input is 8 Lead PDIP compatible with standard CMOS or LSTTL output, down to 3.3V logic. The output drivers feature a high pulse current buffer stage designed for minimum driver cross-conduction. The floating channel can be used to drive an N-channel power MOSFET or IGBT in the high side configuration which operates up to 600 volts.
Typical Connection
up to 600V VCC
V CC
IN SD
VB HO VS LO
TO LOAD
IN SD COM
up to 600V
IR21094 IR2109
HO V CC IN SD V CC IN SD DT V SS RDT V SS COM LO VB VS TO LOAD
(Refer to Lead Assignments for correct configuration). This/These diagram(s) show electrical connections only. Please refer to our Application Notes and DesignTips for proper circuit board layout.
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Absolute maximum ratings indicate sustained limits beyond which damage to the device may occur. All voltage parameters are absolute voltages referenced to COM. The thermal resistance and power dissipation ratings are measured under board mounted and still air conditions.
Symbol
VB VS VHO VCC VLO DT VIN VSS dV S/dt PD
Definition
High side floating absolute voltage High side floating supply offset voltage High side floating output voltage Low side and logic fixed supply voltage Low side output voltage Programmable dead-time pin voltage (IR21094 only) Logic input voltage (IN & SD) Logic ground (IR21094/IR21894 only) Allowable offset supply voltage transient Package power dissipation @ TA +25C (8 Lead PDIP) (8 Lead SOIC) (14 lead PDIP) (14 lead SOIC)
Min.
-0.3 VB - 25 VS - 0.3 -0.3 -0.3 VSS - 0.3 VSS - 0.3 VCC - 25 -50
Max.
625 VB + 0.3 VB + 0.3 25 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 VCC + 0.3 50 1.0 0.625 1.6 1.0 125 200 75 120 150 150 300
Units
V/ns
RthJA
Thermal resistance, junction to ambient
(8 Lead PDIP) (8 Lead SOIC) (14 lead PDIP) (14 lead SOIC)
C/W
TJ TS TL
Junction temperature Storage temperature Lead temperature (soldering, 10 seconds)
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Recommended Operating Conditions
The input/output logic timing diagram is shown in figure 1. For proper operation the device should be used within the recommended conditions. The VS and V SS offset rating are tested with all supplies biased at 15V differential.
Symbol
VB VS VHO VCC VLO VIN DT VSS TA
Definition
High side floating supply absolute voltage High side floating supply offset voltage High side floating output voltage Low side and logic fixed supply voltage Low side output voltage Logic input voltage (IN & SD) Programmable dead-time pin voltage (IR21094 only) Logic ground (IR21094 only) Ambient temperature
Min.
VS + 10 Note 1 VS 10 0 VSS VSS -5 -40
Max.
VS + 20 600 VB 20 VCC VCC VCC 5 125
Units
Note 1: Logic operational for VS of -5 to +600V. Logic state held for VS of -5V to -VBS. (Please refer to the Design Tip DT97-3 for more details).
Dynamic Electrical Characteristics
VBIAS (VCC, VBS) = 15V, VSS = COM, CL = 1000 pF, TA = 25C, DT = VSS unless otherwise specified.
Symbol
ton toff tsd MT tr tf DT MDT
Definition
Turn-on propagation delay Turn-off propagation delay Shut-down propagation delay Delay matching, HS & LS turn-on/off Turn-on rise time Turn-off fall time Deadtime: LO turn-off to HO turn-on(DTLO-HO) & HO turn-off to LO turn-on (DTHO-LO) Deadtime matching = DTLO - HO - DTHO-LO
Min.
400 4
Typ.
750 200 200 0 150 50 540 5 0 0
Max. Units Test Conditions
950 280 280 70 220 80 680 6 60 600 usec nsec nsec VS = 0V VS = 0V RDT= 0 RDT = 200k (IR21094) RDT=0 RDT = 200k (IR21094) VS = 0V VS = 0V or 600V
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Static Electrical Characteristics
VBIAS (VCC , VBS) = 15V, VSS = COM, DT= VSS and TA = 25C unless otherwise specified. The VIL, VIH and IIN parameters are referenced to VSS /COM and are applicable to the respective input leads: IN and SD. The VO, IO and Ron parameters are referenced to COM and are applicable to the respective output leads: HO and LO.
Symbol
VIH VIL VSD,TH+ VSD,THVOH VOL ILK IQBS IQCC IIN+ IINVCCUV+ VBSUV+ VCCUVVBSUVVCCUVH VBSUVH IO+ IO-
Definition
Logic 1 input voltage for HO & logic 0 for LO Logic 0 input voltage for HO & logic 1 for LO SD input positive going threshold SD input negative going threshold High level output voltage, VBIAS - VO Low level output voltage, VO Offset supply leakage current Quiescent VBS supply current Quiescent VCC supply current Logic 1 input bias current Logic 0 input bias current VCC and VBS supply undervoltage positive going threshold VCC and VBS supply undervoltage negative going threshold Hysteresis Output high short circuit pulsed vurrent Output low short circuit pulsed current
Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
2.9 2.9 20 0.4 8.0 7.4 0.3 120 250 0.8 0.3 75 1.0 5 8.9 8.2 0.7 200 350 0.8 0.8 1.4 0.6 50 130 1.6 20 2 9.8 9.0 V VO = 0V, PW 10 s VO = 15V,PW 10 s A mA V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V VCC = 10V to 20V IO = 20 mA IO = 20 mA VB = VS = 600V VIN = 0V or 5V VIN = 0V or 5V RDT = 0 A IN = 5V, SD = 0V IN = 0V, SD = 5V
mA
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Functional Block Diagrams
VB
IR2109
IN
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT HV LEVEL SHIFTER PULSE GENERATOR
UV DETECT R PULSE FILTER R S Q
HO
VS
DEADTIME UV DETECT
VCC
+5V
LO
SD
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT
DELAY
COM
VB
IR21094
IN
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT HV LEVEL SHIFTER PULSE GENERATOR
UV DETECT R PULSE FILTER R S Q
HO
VS
DT
+5V
DEADTIME UV DETECT
VCC
LO
SD
VSS/COM LEVEL SHIFT
DELAY
COM
VSS
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Lead Definitions
Symbol Description
IN SD DT VSS VB HO VS VCC LO COM
Logic input for high and low side gate driver outputs (HO and LO), in phase with HO (referenced to COM for IR2109 and VSS for IR21094)
Logic input for shutdown (referenced to COM for IR2109 and VSS for IR21094) Programmable dead-time lead, referenced to VSS. (IR21094 only) Logic Ground (21094 only) High side floating supply High side gate drive output High side floating supply return Low side and logic fixed supply Low side gate drive output Low side return
Lead Assignments
1 2 3 4 VCC IN SD COM VB HO VS LO
8
7 6 5
1 2 3 4
VCC IN SD COM
VB HO VS LO
8
7 6 5
8 Lead PDIP
8 Lead SOIC
IR2109
IR2109S
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
VCC IN SD DT VSS COM LO VB HO VS
14
13 12 11 10 9 8
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
VCC IN SD DT VSS COM LO VB HO VS
14
13 12 11 10 9 8
14 Lead PDIP
14 Lead SOIC
IR21094
6
IR21094S
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
IN
IN(LO)
50% 50%
SD
IN(HO)
ton tr 90% toff 90% tf
HO LO
LO HO
Figure 1. Input/Output Timing Diagram
10%
10%
Figure 2. Switching Time Waveform Definitions
SD
50%
50%
50%
IN
tsd
90%
HO LO
90%
HO LO
DT LO-HO 90%
10% DT HO-LO
Figure 3. Shutdown Waveform Definitions
MDT= DT LO-HO
10% - DTHO-LO
IN (LO)
50% 50%
Figure 4. Deadtime Waveform Definitions
IN (HO)
LO
HO
10%
MT 90%
MT
LO
HO
Figure 5. Delay Matching Waveform Definitions
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
1300
1300
Turn-on Propagation Delay (ns)
Turn-on Propagation Delay (ns)
1100
1100
Max.
900
Ma x
900 T yp. 700
700
T yp.
500 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
500 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 6A. Turn-on Propagation Delay vs. Temperature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 6B. Turn-on Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
500
500
Turn-of f Propagation Delay (ns)
Turn-of f Propagation Delay (ns)
400
400 Ma x. T yp. 200
300 Ma x. 200 T yp. 100
300
100
0 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
0 75 100 125 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature ( C)
Figure 7A. Turn-off Propagation Delay vs. Temperature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 7B. Turn-off Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
500
500
SD Propagation Delay (ns)
SD Propagation Delay (ns)
400
400 Max. 300 T yp. 200
300 Max. 200 T yp. 100
100
0 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
0 75 100 125 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature ( C)
Figure 8A. SD Propagation Delay vs. Temperature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 8B. SD Propagation Delay vs. Supply Voltage
500
500
Turn-on Rise Time (ns)
Turn-on Rise Time (ns)
400
400
300
300
Max. T yp.
200
Max. T yp.
200
100
100
0 -5 0 -25 0 25 50 75 1 00 125
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 9A. Turn-on Rise Time vs. Temperature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 9B. Turn-on Rise Time vs. Supply Voltage
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
200
200
Turn-off Fall Time (ns)
Turn-off Fall Time (ns)
150
150
100 Ma x. 50 T yp. 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
100
Max.
T yp. 50
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 10A. Turn-off Fall Time vs. Temperature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 10B. Turn-off Fall Time vs. Supply Voltage
1000
1000
800
800 Ma x.
Deadtime (ns)
Deadtime (ns)
Ma x.
600 T yp. 400 Min.
600
T yp.
Min. 400
200 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
200 10 12 14 16 18 20
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 11A. Deadtime vs. Temperature
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 11B. Deadtime vs. Supply Volta ge
10
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Logic "1" Input Voltage (V)
6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 50 100 150 200 M ax. T yp. M in.
4 Max. 3
Deadtime ( s)
0 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
75
100
125
RDT (K)
Figure 11C. Deadtime vs. RDT (IR21094 only)
Temperature ( C)
Figure 12A. Logic 1 Input Voltage vs. Temperature
Logic "1" Input Voltage (V)
Logic "0" Input Voltage (V)
4 Ma x.
Min.
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 12B. Logic 1 Input Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 13A. Logic 0 Input Voltage vs. Temperature
www.irf.com
11
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
SD Positive Going Threshold (V)
Logic "0" Input Voltage (V)
Max.
Min.
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 13B. Logic 0 Input Current vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature (oC)
Figure 14A. SD Positive Going Threshold vs. Temperature
SD Negative Going Threshold (V)
SD Positive Going Threshold (V)
4 Ma x.
Min.
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 14B. SD Positive Going Threshold vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 15A. SD Negative Going Threshold vs. Temperature
12
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
SD Negative Going Threshold (V)
High Level Output Voltage (V)
12 14 16 18 20
Min.
M ax. T yp.
0 10
0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 15B. SD Negative Going Threshold vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 16A. High Level Output Voltage vs. Temperature
1.5
High Level Output Voltage (V)
Low Level Output Voltage (V)
1.2
0.9
Max.
0.6 Max. 0.3 T yp. 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
T yp. 1
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 16B. High Level Output Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 17A. Low Level Output Voltage vs. Temperature
www.irf.com
13
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Offset Supply Leakage Current ( A)
1.5
500
Low Level Output Voltage (V)
1.2
400
0.9 Ma x. 0.6 T yp. 0.3
300
200
100 Ma x. 0 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
75
100
125
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 17B. Low Level Output Voltage vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( C)
Figure 18A. Offset Supply Leakage Current vs. Temperature
Of f set Supply Leakage Current ( A)
500
400
400
V BS Supply Current ( A)
300
300
200
200
100
Max. T yp. Min.
100
Max.
0 0 100 200 300 400 500 600
0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
V B Boost Voltage (V)
Temperature ( oC)
igure 18B. Offset Supply Leakage Current vs. Boost Voltage
Figure 19A. VBS Supply Current vs. Temperature
14
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
400
3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 T yp. 1.0 0.5 0.0
10 12 14 16 18 20
300
Vcc Supply Current (mA)
V B S Supply Current ( A)
Max.
200
100
Max . T yp. Min.
Min.
-50
-25
25
50
75
100
125
V BS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 19B. VBS Supply Current vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 20A. VCC Supply Current vs. Temperature
3.0
60
Logic "1" Input Current ( A)
V CC Supply Current (mA)
2.5
50
2.0
40
1.5 1.0 0.5 Max. T yp. Min.
30
20 Max. T yp. 0 -50 -25 0 25 50 75 100 125
10
0.0 10 12 14 16 18 20
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Temperature (oC)
Fi
21A L
i "1" I
Figure 20B. VCC Supply Current vs. VCC Supply Voltage
Figure 21A. Logic 1 Input Current vs. Temperature
www.irf.com
15
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
60
Logic "1" Input Current ( A)
Logic "0" Input Current ( A)
12 14 16 18 20
50
40 30 20 10 Max.
3 Max. 2
T yp.
0 10
0 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
75
100
125
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 21B. Logic 1 Input Current vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( C)
Figure 22A. Logic 0 Input Current vs. Temperature
12
V CC UVLO Threshold (+) (V)
Logic "0" Input Current ( A)
11
3 Ma x. 2
10
Ma x.
T yp.
Min.
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
7 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
75
100
125
V CC Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 22B. Logic 0 Input Currentt vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( C)
Figure 23. VCC Undervoltage Threshold (+) vs. Temperature
16
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
11
12
V BS UVLO Threshold (+) (V)
0 25 50 75 100 125
V CC UVLO Threshold (-) (V)
10 Max. T yp. 8 Min. 7
11 Max.
10
T yp.
Min.
6 -50 -25
7 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
75
100
125
Temperature ( oC)
Figure 24. VCC Undervoltage Threshold (-) vs. Temperature
Temperature ( C)
Figure 25. VBS Undervoltage Threshold (+) vs. Temperature
11
500
V BS UVLO Threshold (-) (V)
Output Source Current ( A)
10 Max. T yp. 8 Min. 7
400
300 T yp. 200 Min. 100
6 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
75
100
125
-50
-25
25
50
o
75
100
125
Temperature ( C)
Figure 26. VBS Undervoltage Threshold (-) vs. Temperature
Temperature ( C)
Figure 27A. Output Source Current vs. Temperature
www.irf.com
17
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
500
600 500 T yp. 400 300 200 100 0 10 12 14 16 18 20 -50 -25 0 25 50
o
Output Source Current ( A)
400
300
Output Sink Current ( A)
Min.
200 T yp. 100 Min. 0
75
100
125
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 27B. Output Source Current vs. Supply Voltage
Temperature ( C)
Figure 28A. Output Sink Current vs. Temperature
600
Output Sink Current ( A)
500
V S Offset Supply Voltage (V)
-2 T yp. -4
400
300 T yp. 200 Min.
-6
-8
100
0 10 12 14 16 18 20
-10 10 12 14 16 18 20
V BIAS Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 28B. Output Sink Currentt vs. Supply Voltage
V BS Flouting Supply Voltage (V)
Figure 29. Maximum VS Negative Offset vs. Supply Voltage
18
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 120 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 30. IR2109 vs Frequency (IRFBC20) Rgate = 33W, VCC = 15V
140V 70V 0V
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 31. IR2109 vs Frequency (IRFBC30) Rgate = 22W, VCC = 15V
140V 70V 0V
o Temprature ( C)
140 120
o Temperature ( C)
140 120
o Temperature ( C)
140V 70V 0V
140V 70V
0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000
1000
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 32. IR2109 vs Frequency (IRFBC40) Rgate = 15W, VCC = 15V
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 33. IR2109 vs Frequency (IRFPE50) Rgate = 10W, VCC = 15V
www.irf.com
19
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 34. IR21094 vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
140 120
o Temperature ( C)
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 35. IR21094 vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate=22 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
140 120
o Temperature ( C)
140 120 Temperature (oC) 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
140V
140V
70V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 36. IR21094 vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
70V 0V
0V
1000
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 37. IR21094 vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
20
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 120 Temperature (oC)
o Temperature ( C)
140 120
140V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 38. IR2109S vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
70V 0V
1000
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 39. IR2109S vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate=22 , V CC=15V
140 120
o Temperature ( C)
140V70V
140 120 Tempreture (oC)
140V 70V 0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100
0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000
1000
Frequency (KHz)
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 40. IR2109S vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
Figure 41. IR2109S vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
www.irf.com
21
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
140 120 Temperature (oC)
Temperature (oC)
140 120 100 80 60 40 20
140V 70V 0V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 42. IR21094S vs. Frequency (IRFBC20), Rgate=33 , V CC=15V
140V 70V 0V
10
100
1000
Frequency (KHz)
Figure 43. IR21094S vs. Frequency (IRFBC30), Rgate=22 , V CC=15V
140 Temperature (oC)
140 120 Temperature (oC)
140V 70V 0V
140V 70V 0V
120 100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 44. IR21094S vs. Frequency (IRFBC40), Rgate=15 , V CC=15V
100 80 60 40 20 1 10 100 1000 Frequency (KHz)
Figure 45. IR21094S vs. Frequency (IRFPE50), Rgate=10 , V CC=15V
22
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Case Outlines
8 Lead PDIP
01-6014 01-3003 01 (MS-001AB)
D A 5
B
F OOT PRINT 8X 0.72 [.028]
DIM A b c D
INCHES MIN .0532 .013 .0075 .189 .1497 MAX .0688 .0098 .020 .0098 .1968 .1574
MILLIMETERS MIN 1.35 0.10 0.33 0.19 4.80 3.80 MAX 1.75 0.25 0.51 0.25 5.00 4.00
A1 .0040
6 E
5 H 0.25 [.010] A
E
6.46 [.255]
e e1 H K L
8X 1.78 [.070]
.050 BAS IC .025 BAS IC .2284 .0099 .016 0 .2440 .0196 .050 8
1.27 BAS IC 0.635 BAS IC 5.80 0.25 0.40 0 6.20 0.50 1.27 8
6X
e e1
3X 1.27 [.050]
K x 45
C 0.10 [.004]
y 8X c
8X b 0.25 [.010]
NOT ES :
A1 C A B
8X L 7
1. DIMENSIONING & TOLE RANCING PER AS ME Y14.5M-1994. 2. CONT ROLLING DIMENSION: MILLIME TER 3. DIMENSIONS ARE S HOWN IN MILLIMET ERS [INCHE S]. 4. OUTLINE CONFORMS T O JEDEC OUT LINE MS-012AA.
5 DIMENS ION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROT RUS IONS. MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT T O E XCEED 0.15 [.006]. 6 DIMENS ION DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD PROT RUS IONS. MOLD PROTRUSIONS NOT T O E XCEED 0.25 [.010]. 7 DIMENS ION IS T HE LE NGT H OF LEAD FOR SOLDERING T O A SUBS TRAT E.
8 Lead SOIC
www.irf.com
01-6027 01-0021 11 (MS-012AA)
23
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
14 Lead PDIP
01-6010 01-3002 03 (MS-001AC)
14 Lead SOIC (narrow body)
01-6019 01-3063 00 (MS-012AB)
Data and specifications subject to change without notice. 7/11/2003
24
www.irf.com
IR2109(4) (S) & (PbF)
Basic Part (Non-Lead Free) 8-Lead PDIP IR2109 8-Lead SOIC IR2109S 14-Lead PDIP IR21094 14-Lead SOICIR21094S order order order order IR2109 IR2109S IR21094 IR21094S
Lead-Free Part 8-Lead PDIP IR2109 8-Lead SOIC IR2109S 14-Lead PDIP IR21094 14-Lead SOIC IR21094S order order order order IR2109PbF IR2109SPbF IR21094PbF IR21094SPbF
This product has been designed and qualified for the Industrial market. Qualification Standards can be found on IRs Website. Data and specifications subject to change without notice. IR WORLD HEADQUARTERS: 233 Kansas St., El Segundo, California 90245, USA Tel: (310) 252-7105 TAC Fax: (310) 252-7903 Visit us at www.irf.com for sales contact information.09/08/04 www.irf.com 25
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Ir 2184Documento24 pagineIr 2184buiphuoclaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2108Documento23 pagineIr 2108robertofurlancriNessuna valutazione finora
- Half-Bridge Driver (S) : Features Product SummaryDocumento9 pagineHalf-Bridge Driver (S) : Features Product SummaryMahmoued YasinNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir2181 Igbt Driver PDFDocumento21 pagineIr2181 Igbt Driver PDFismifaizulNessuna valutazione finora
- IR2110/IR2113: High and Low Side DriverDocumento16 pagineIR2110/IR2113: High and Low Side DriverguiknopNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2104Documento14 pagineIr 2104Néstor BernalNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2110Documento17 pagineIr 2110Nguyen KhangNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2010Documento17 pagineIr 2010Naveed AhmedNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2127Documento16 pagineIr 2127kimonspNessuna valutazione finora
- IR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SDocumento15 pagineIR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SPandu Sandi PratamaNessuna valutazione finora
- Irs 2103Documento14 pagineIrs 2103Việt LêNessuna valutazione finora
- Irs 2184 DatasheetDocumento30 pagineIrs 2184 DatasheetphieuxuatkhoNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2113Documento18 pagineIr 2113rohitsingh2909Nessuna valutazione finora
- IR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SDocumento15 pagineIR2110/IR2113 : High and Low Side Driver SPepe ModstNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2111Documento15 pagineIr 2111Miltongrimi GrimilNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir2103 DatasheetDocumento12 pagineIr2103 DatasheetToma HaiNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2101Documento14 pagineIr 2101Willard DmpseyNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir2117 Igbt Driver PDFDocumento18 pagineIr2117 Igbt Driver PDFismifaizulNessuna valutazione finora
- S2127Documento21 pagineS2127RICHIHOTS2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2111Documento15 pagineIr 2111Kutsal KaraNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2213Documento14 pagineIr 2213Lampros LampropoulosNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Audio Driver With Discrete Dead-Time and ProtectionDocumento25 pagineDigital Audio Driver With Discrete Dead-Time and Protectiongotcha75Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2103Documento18 pagineIr 2103Hồ Trung ChíNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2105Documento12 pagineIr 2105Manuel Villegas AcostaNessuna valutazione finora
- Features Packages: Data Sheet No. PD60161-PDocumento18 pagineFeatures Packages: Data Sheet No. PD60161-PPafuncio de AlecrimNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2304Documento8 pagineIr 2304Rajo AmehNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2153Documento9 pagineIr 2153SteveAbonyiNessuna valutazione finora
- Irs2101 (S) PBF: High and Low Side DriverDocumento15 pagineIrs2101 (S) PBF: High and Low Side Driverdesin01Nessuna valutazione finora
- Self-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver: Ir2153 (D) (S) & (PBF)Documento9 pagineSelf-Oscillating Half-Bridge Driver: Ir2153 (D) (S) & (PBF)Zoltán HalászNessuna valutazione finora
- High and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryDocumento14 pagineHigh and Low Side Driver: Features Product SummaryFernando Camargo100% (1)
- Irs 20965Documento16 pagineIrs 20965Eduardo CruzNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverDocumento17 pagineIr2112 (S) & (PBF) : High and Low Side DriverMugahed DammagNessuna valutazione finora
- FAN7382 High-And Low-Side Gate Driver: Features DescriptionDocumento15 pagineFAN7382 High-And Low-Side Gate Driver: Features DescriptionRiza BaduaNessuna valutazione finora
- Datasheet 2Documento12 pagineDatasheet 2Alex Navas FonsecaNessuna valutazione finora
- Features Product Summary: Led Buck Regulator Control IcDocumento20 pagineFeatures Product Summary: Led Buck Regulator Control IcJess AJNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir 2153Documento9 pagineIr 2153Carlos Marinho SilvaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ca3260, Ca3260A: 4Mhz, Bimos Operational Amplifier With Mosfet Input/Cmos Output FeaturesDocumento4 pagineCa3260, Ca3260A: 4Mhz, Bimos Operational Amplifier With Mosfet Input/Cmos Output FeaturesPaulo Cesar SimonettiNessuna valutazione finora
- Fan 7361Documento9 pagineFan 7361Odalis CabaNessuna valutazione finora
- FAN73832 (Half-Bridge Dead Time Control)Documento16 pagineFAN73832 (Half-Bridge Dead Time Control)Ismael StarkNessuna valutazione finora
- Features Applications: SBOS141Documento11 pagineFeatures Applications: SBOS141eslovenitNessuna valutazione finora
- Ir2153 2 PDFDocumento9 pagineIr2153 2 PDFamijoski6051Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fan 7392NDocumento18 pagineFan 7392NKhaleel MohammadNessuna valutazione finora
- IRS2092 DatasheetDocumento18 pagineIRS2092 DatasheetSergio Daniel BarretoNessuna valutazione finora
- CA3240Documento16 pagineCA3240Jorge NovoaNessuna valutazione finora
- 8 Pin Ic - FSQ510Documento15 pagine8 Pin Ic - FSQ510Raja Pathamuthu.GNessuna valutazione finora
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsDa EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Nessuna valutazione finora
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Da EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Valutazione: 2.5 su 5 stelle2.5/5 (3)
- Electricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeDa EverandElectricity in Fish Research and Management: Theory and PracticeNessuna valutazione finora
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsDa EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (6)
- Diode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesDa EverandDiode, Transistor & Fet Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesValutazione: 4.5 su 5 stelle4.5/5 (7)
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDa EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Power Electronics and ApplicationsDa EverandDigital Power Electronics and ApplicationsValutazione: 3.5 su 5 stelle3.5/5 (3)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorDa Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorValutazione: 4 su 5 stelle4/5 (1)
- Switching in Electrical Transmission and Distribution SystemsDa EverandSwitching in Electrical Transmission and Distribution SystemsNessuna valutazione finora
- SEW 5500CB Datasheet PDFDocumento2 pagineSEW 5500CB Datasheet PDFSaul Pablo Maita FarfanNessuna valutazione finora
- LCDDocumento11 pagineLCDNikhith Reddy100% (1)
- PMR446Documento2 paginePMR446SultanNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Electronics RK Kanodia & Ashish Murolia PDFDocumento487 pagineDigital Electronics RK Kanodia & Ashish Murolia PDFshashank gupta75% (8)
- Free Governor Mode of OperationDocumento12 pagineFree Governor Mode of Operationlrpatra100% (2)
- Xilinx LogiCoreDocumento3 pagineXilinx LogiCorePaul CasaleNessuna valutazione finora
- UL General-Use Circuit Ampacity Reference ChartDocumento2 pagineUL General-Use Circuit Ampacity Reference ChartDaniel KretsuNessuna valutazione finora
- Silcopac D: Hardware SOFTWARE Basic Version BDocumento2 pagineSilcopac D: Hardware SOFTWARE Basic Version BGerardo BaltaNessuna valutazione finora
- Smartpack (DS-242100.100.DS3-1-7) .APR.09Documento2 pagineSmartpack (DS-242100.100.DS3-1-7) .APR.09samsungaceplusNessuna valutazione finora
- SYS VoomPC 2 Intel D2700MUD ManualDocumento4 pagineSYS VoomPC 2 Intel D2700MUD Manualbobmartin00Nessuna valutazione finora
- SMD Type Diodes: Schottky Diodes SS1020 SS10100Documento2 pagineSMD Type Diodes: Schottky Diodes SS1020 SS10100Momo MendozaNessuna valutazione finora
- Hydra: The Versatile DoorDocumento14 pagineHydra: The Versatile DoorAnnabella RossiniNessuna valutazione finora
- CoreIP ClockDocumento81 pagineCoreIP ClockPortgasD.AceNessuna valutazione finora
- Generator SynchronisationDocumento12 pagineGenerator SynchronisationTapas Chaudhuri100% (1)
- Wiring Headlight RelaysDocumento20 pagineWiring Headlight RelaysFloris van EnterNessuna valutazione finora
- DFT Report For Sequence DetectorDocumento11 pagineDFT Report For Sequence DetectorShravan KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- UsefulLife - Protective RelaysDocumento6 pagineUsefulLife - Protective Relaysgulatimanish1985Nessuna valutazione finora
- Numerazione Bosch PDFDocumento4 pagineNumerazione Bosch PDFssasNessuna valutazione finora
- Static Electricity - Tool BoxDocumento12 pagineStatic Electricity - Tool Boxyvk004Nessuna valutazione finora
- Futaba Catalog 2007 PDFDocumento36 pagineFutaba Catalog 2007 PDFMarcos AldrovandiNessuna valutazione finora
- OpenSimwheel TutorialDocumento33 pagineOpenSimwheel TutorialznamNessuna valutazione finora
- Lect10 - Receiver Noise and BERDocumento12 pagineLect10 - Receiver Noise and BERARCHIT SUNDLINessuna valutazione finora
- HBL BatteriesDocumento36 pagineHBL BatteriesDebnath Roychowdhury100% (1)
- 50 - 100kV - AC Dielectric Test SetDocumento4 pagine50 - 100kV - AC Dielectric Test SetlrpatraNessuna valutazione finora
- CLAA102NA0ACWDocumento16 pagineCLAA102NA0ACWIvan BenginNessuna valutazione finora
- Orthophos XG 3, Installation ManualDocumento146 pagineOrthophos XG 3, Installation ManualNuriddin khabirovNessuna valutazione finora
- Enc Inverter: Shenzhen Encom Electric Technologies Co., LTDDocumento16 pagineEnc Inverter: Shenzhen Encom Electric Technologies Co., LTDMr CdtNessuna valutazione finora
- Digital Energy GT Series: User ManualDocumento20 pagineDigital Energy GT Series: User ManualWilton AlvesNessuna valutazione finora
- 194 Construction, Laying and Installation Techniques For Extruded and Self-Contained Fluid Filled Cable Systems PDFDocumento147 pagine194 Construction, Laying and Installation Techniques For Extruded and Self-Contained Fluid Filled Cable Systems PDFAkhil Anumandla100% (1)
- MDR 2 DRH 4189340300i Uk 6852 Taptin0Documento26 pagineMDR 2 DRH 4189340300i Uk 6852 Taptin0wan jspNessuna valutazione finora