Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
MCTD 3
Caricato da
Laksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
MCTD 3
Caricato da
Laksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelCopyright:
Formati disponibili
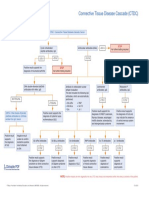
Connective Tissue Disease Testing
Click here for topics associated with this algorithm
INDICATIONS FOR TESTING
Patient with systemic symptoms
(arthritis, arthralgias, skin rashes, anemia, renal dysfunction, pleuritis, pericarditis)
False-positive results
Anti-Nuclear Antibodies may be induced by
(ANA), IgG by ELISA* age, certain infections,
cancers, and drugs
negative positive
ANA may be positive in
inflammatory diseases
such as autoimmune
Possible scenarios liver diseases
No connective tissue disease (CTD)
False-negative result – consider SSc, PM/DM or
ANA (HEp-2), IgG by
inactive SLE
IFA
If suspicion for CTD is strong, consider testing
for disease-specific antibody tests or panels
Centromere Cytoplasmic Peripheral/rim/ Nucleolar Speckled
pattern pattern homogenous pattern pattern pattern
lcSSc, PM/DM, SLE, SSc,
SLE, DIL
CREST SLE, SSc PM/DM
SS-A /SS-B+ U1RNP+ Scl-70+ No specificity**
Sm+
SLE SLE, SjS MCTD/UCTD dcSSc
Antibody Key Disease legend
CREST CREST syndrome (calcinosis, Raynaud phenomenon,
esophageal dysmotility, sclerodactyly and telangiectasia)
RNP RNP (U1) (Ribonucleic Protein) (ENA)
DIL Drug-induced lupus erythematosus
Antibody, IgG
dcSSc Diffuse cutaneous scleroderma
Scl-70 Scleroderma (Scl-70) (ENA) Antibody, IgG
lcSSc Limited cutaneous scleroderma
Sm Sm (ENA) Antibody, IgG
SS-A SS-A (Ro) (ENA) Antibody, IgG MCTD/UCTD Mixed connective tissue disease/Undifferentiated
SS-B SS-B (La) (ENA) Antibody, IgG connective tissue disease
PM/DM Polymyositis/Dermatomyositis
SjS Sjögren syndrome
SLE Systemic lupus erythematosus
SSc Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis)
* ELISA screen detects antibodies against dsDNA, histone, SS-A (Ro), SS-B (La), Sm, RNP, Scl-70, Jo-1, centromere, and an extract of lysed
HEp-2 cells
** Unidentified specificities or markers of low prevalence in CTD
Note: Overlap may occur among the antibodies and disesases. Associations between ANA IFA pattern and disorders such as autoimmune
hepatitis (AIH) and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) are not indicated
© 2006-2012 ARUP Laboratories. All Rights Reserved. Revised 9/12/2012 www.arupconsult.com
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Connective Tissue DZDocumento1 paginaConnective Tissue DZAndre GarciaNessuna valutazione finora
- Connective Tissue Disease CascadeDocumento1 paginaConnective Tissue Disease CascadeYustina BubnovaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antinuclear Antibodies: When To Test and How To Interpret FindingsDocumento4 pagineAntinuclear Antibodies: When To Test and How To Interpret FindingsFariz NurNessuna valutazione finora
- Unknown Author - AutoantibodypdfDocumento7 pagineUnknown Author - AutoantibodypdfBhupi AgrawalNessuna valutazione finora
- Atlas Patrones ANADocumento56 pagineAtlas Patrones ANAkemitaNessuna valutazione finora
- ANA PatternDocumento2 pagineANA PatternNayem comNessuna valutazione finora
- 2018 AIRImmu 02Documento12 pagine2018 AIRImmu 02Cheng-Ting WuNessuna valutazione finora
- SolidTumors SporadicDocumento2 pagineSolidTumors SporadicPhoebe AjeroNessuna valutazione finora
- ANA TestDocumento16 pagineANA TestSami Al WesabiNessuna valutazione finora
- Sysemic Lupus Erythematosus Case StudyDocumento53 pagineSysemic Lupus Erythematosus Case StudyJennylen Torres100% (1)
- Paraneoplastic Syndrome of CNSDocumento71 pagineParaneoplastic Syndrome of CNSpreeti sharmaNessuna valutazione finora
- Last Look Nephrology & Rheumatology (Medicine Must Know)Documento43 pagineLast Look Nephrology & Rheumatology (Medicine Must Know)rohankananiNessuna valutazione finora
- Overlap Syndromes v2Documento32 pagineOverlap Syndromes v2JerryEddyaPutraBoerNessuna valutazione finora
- Motor Neurone Disease PDFDocumento4 pagineMotor Neurone Disease PDFTONY GO AWAYNessuna valutazione finora
- Spektrum AIDocumento55 pagineSpektrum AIOgizWaraNessuna valutazione finora
- List of AbbreviationsDocumento1 paginaList of AbbreviationsFlea CidNessuna valutazione finora
- Aspect Lab Autoimun1Documento55 pagineAspect Lab Autoimun1Juliana SanjayaNessuna valutazione finora
- Overlap Syndromes: Key PointsDocumento23 pagineOverlap Syndromes: Key PointsAddie EspirituNessuna valutazione finora
- Antinuclear Antibody ANADocumento3 pagineAntinuclear Antibody ANAanaelisabetapNessuna valutazione finora
- Autoantibodies: Prof Sami Salman, FRCP, MRCP, DMR, Ces, MB CHBDocumento40 pagineAutoantibodies: Prof Sami Salman, FRCP, MRCP, DMR, Ces, MB CHBamereNessuna valutazione finora
- By S.Dharaniya, 3 Year BiotechnologyDocumento14 pagineBy S.Dharaniya, 3 Year BiotechnologyrevaishNessuna valutazione finora
- Supervisor: Prof. Dr. Atan Baas Sinuhaji, Spa (K)Documento35 pagineSupervisor: Prof. Dr. Atan Baas Sinuhaji, Spa (K)Ranap HadiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Referat IKA Spinal Muscular AtrophyDocumento30 pagineReferat IKA Spinal Muscular AtrophycindyNessuna valutazione finora
- Impact of Bone Marrow Fibrosis and Early Response on Outcome after Azacitidine Therapy in 94 Patients with Myelodisplastic Syndromes, Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Blood | American Society of HematologyDocumento5 pagineImpact of Bone Marrow Fibrosis and Early Response on Outcome after Azacitidine Therapy in 94 Patients with Myelodisplastic Syndromes, Chronic Myelomonocytic Leukemia and Acute Myeloid Leukemia | Blood | American Society of HematologymaomaochongNessuna valutazione finora
- EUROLINE Myositis Profi Le 3 (IgG) SummaryDocumento2 pagineEUROLINE Myositis Profi Le 3 (IgG) SummaryShahid Hussain100% (1)
- ANA Patterns PDFDocumento4 pagineANA Patterns PDFLucia OlosuteanNessuna valutazione finora
- Nerve Conduction and Electromyography StudiesDocumento7 pagineNerve Conduction and Electromyography StudiesMaríaFernandaEcheverryNessuna valutazione finora
- SEMINAR 1 - Autoimmune Diseases and Immunodeficiency DisordersDocumento12 pagineSEMINAR 1 - Autoimmune Diseases and Immunodeficiency DisordersAprille PatolNessuna valutazione finora
- L7 Is AutoimmunityDocumento3 pagineL7 Is AutoimmunityErickson MoragaNessuna valutazione finora
- Insert Kit Anti dsDNADocumento2 pagineInsert Kit Anti dsDNAsitirahmawatiningsih25Nessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-Dsdna-Ncx Elisa (Igg) Test Instruction: Summary and ExplanationDocumento12 pagineAnti-Dsdna-Ncx Elisa (Igg) Test Instruction: Summary and Explanationanahh ramakNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheumatological Antibodies PDFDocumento1 paginaRheumatological Antibodies PDFewqeNessuna valutazione finora
- Poliartrita Reumatoida: Partea A DouaDocumento83 paginePoliartrita Reumatoida: Partea A DouaAlexandra CojocaruNessuna valutazione finora
- Anti-dsDNA Antibody Isotypes in Systemic Lupus, IgADocumento8 pagineAnti-dsDNA Antibody Isotypes in Systemic Lupus, IgAPuri RahmawatiNessuna valutazione finora
- Antigen Class 0 (+) + ++ +++Documento2 pagineAntigen Class 0 (+) + ++ +++Buat DownloadNessuna valutazione finora
- ANA Patterns EuroimmuneDocumento4 pagineANA Patterns EuroimmuneManuel ArenasNessuna valutazione finora
- Toronto cxk1Documento17 pagineToronto cxk1Nguyễn TiếnNessuna valutazione finora
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroDocumento5 pagineSystemic Lupus Erythematosus Case: Pathogenisis:: NmcastroAngelo ErispeNessuna valutazione finora
- Neuromuscular Junction Disorders: Myasthenia GravisDocumento20 pagineNeuromuscular Junction Disorders: Myasthenia GravisIzabella MihályNessuna valutazione finora
- Clinical and Genetic Overview of Paroxysmal Moveme PDFDocumento55 pagineClinical and Genetic Overview of Paroxysmal Moveme PDFRomy ZgheibNessuna valutazione finora
- AutoantibodiesDocumento13 pagineAutoantibodiesCristina ElenaNessuna valutazione finora
- Autoimmune DiseasesDocumento1 paginaAutoimmune DiseasesFrances FranciscoNessuna valutazione finora
- Autoimmune Disease Study GuideDocumento2 pagineAutoimmune Disease Study GuidenickfemanNessuna valutazione finora
- Plasma Cell Dyscrasias Testing Algorithm PDFDocumento1 paginaPlasma Cell Dyscrasias Testing Algorithm PDFolesyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Antibodies Associated With Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes - UpToDateDocumento2 pagineAntibodies Associated With Paraneoplastic Neurologic Syndromes - UpToDateFernandoNessuna valutazione finora
- Rheumatology I 03 Connective Tissue DiseasesDocumento20 pagineRheumatology I 03 Connective Tissue DiseasesWen Jie LauNessuna valutazione finora
- New Paradigm in Lupus Erythematosus Systemic ManagementDocumento79 pagineNew Paradigm in Lupus Erythematosus Systemic ManagementALUCARD 1442Nessuna valutazione finora
- Antinuclear Antibodies Marker of Diagnosis and Evolution in Autoimmune DiseasesDocumento12 pagineAntinuclear Antibodies Marker of Diagnosis and Evolution in Autoimmune DiseasesFAIZAN KHANNessuna valutazione finora
- Diagnostics 10 00779 PDDocumento16 pagineDiagnostics 10 00779 PDLateepheart YakubNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture6 - Personalized Genomics 2019Documento208 pagineLecture6 - Personalized Genomics 2019Charlie HouNessuna valutazione finora
- DR Adrian Jones - Seronegative SpondyloarthropathiesDocumento38 pagineDR Adrian Jones - Seronegative SpondyloarthropathiesMaryam ShahbazNessuna valutazione finora
- RJN 2017 2 Art-04Documento3 pagineRJN 2017 2 Art-04Ana GabrielaNessuna valutazione finora
- Blood Donor SelectionDocumento15 pagineBlood Donor SelectionKat JornadalNessuna valutazione finora
- Contoh Kasus MCTDDocumento3 pagineContoh Kasus MCTDElva KadarhadiNessuna valutazione finora
- SLEDocumento6 pagineSLEStefhanie Mae LazaroNessuna valutazione finora
- Spondyloarthritides - Dr. SyDocumento2 pagineSpondyloarthritides - Dr. SyMACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTENessuna valutazione finora
- List of Important Topics For NEET PG by DbmciDocumento7 pagineList of Important Topics For NEET PG by Dbmcimanmohansai bache57% (7)
- Nephrotic Syndrome PDF 2Documento2 pagineNephrotic Syndrome PDF 2MNessuna valutazione finora
- Neurodegenerative Diseases: Multifactorial Degenerative Processes, Biomarkers and Therapeutic ApproachesDa EverandNeurodegenerative Diseases: Multifactorial Degenerative Processes, Biomarkers and Therapeutic ApproachesNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation JurnalDocumento36 paginePresentation JurnalLaksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal Endokrin IDocumento7 pagineJurnal Endokrin ILaksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelNessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal PulmoDocumento13 pagineJurnal PulmoLaksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelNessuna valutazione finora
- Mechanisms of Insulin ActionDocumento13 pagineMechanisms of Insulin ActionLaksmita Ayu Dewi TetanelNessuna valutazione finora
- Exploratory LaparotomyDocumento13 pagineExploratory LaparotomyCj Atto100% (1)
- Human Resource ManagementDocumento18 pagineHuman Resource ManagementT S Kumar KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Crime Report.1 1 UpdatedDocumento2 pagineCrime Report.1 1 UpdatedArgie DionioNessuna valutazione finora
- Pulse OximetryDocumento2 paginePulse OximetryRaja AnuNessuna valutazione finora
- Own Dietary AssessmentDocumento16 pagineOwn Dietary AssessmentShefali RawatNessuna valutazione finora
- The Humorous Rewriting of Orwells 1984 The GreekDocumento16 pagineThe Humorous Rewriting of Orwells 1984 The GreeknuriaNessuna valutazione finora
- Child Abuse - MeghaDocumento9 pagineChild Abuse - MeghameghaudayanNessuna valutazione finora
- LapiDocumento38 pagineLapiYuliSetiyantoNessuna valutazione finora
- Argumentative Writing - PresentationDocumento2 pagineArgumentative Writing - PresentationMaria Cecilia Annette RahardjaNessuna valutazione finora
- Sa CHNDocumento34 pagineSa CHNKiahana PascualNessuna valutazione finora
- Claims of Fact, Policy and ValueDocumento7 pagineClaims of Fact, Policy and ValueGreggy LatrasNessuna valutazione finora
- Vaccine TextDocumento2.739 pagineVaccine TextMark Mast0% (2)
- ENG 111-054 - Legalized Euthanasia As Opposed To HospiceDocumento5 pagineENG 111-054 - Legalized Euthanasia As Opposed To HospiceBee ThaoNessuna valutazione finora
- dm2022 0384Documento4 paginedm2022 0384Jason David V. NazarenoNessuna valutazione finora
- Custodial Supervisor Cover LetterDocumento5 pagineCustodial Supervisor Cover Letterfujowihesed2100% (2)
- Catering ManagementDocumento5 pagineCatering ManagementWc-mark ChuvachucHuNessuna valutazione finora
- Project Scenario - Learn-ITDocumento3 pagineProject Scenario - Learn-ITshix cutieNessuna valutazione finora
- Working Phase 1st Day Npi (Psychosis)Documento3 pagineWorking Phase 1st Day Npi (Psychosis)Honey Bee S. PlatolonNessuna valutazione finora
- Aesthetic Inlays: November 2011Documento4 pagineAesthetic Inlays: November 2011Diego SarunNessuna valutazione finora
- Resistance Training: FW01 Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 1Documento7 pagineResistance Training: FW01 Physical Activities Toward Health and Fitness 1Jerome SadulloNessuna valutazione finora
- LSI Brgy. CertificationDocumento2 pagineLSI Brgy. CertificationRuth BolongaitaNessuna valutazione finora
- Steps in The Self Exploration ProcessDocumento3 pagineSteps in The Self Exploration Processrezzel montecilloNessuna valutazione finora
- MiscarriageDocumento38 pagineMiscarriagezianab aliNessuna valutazione finora
- ReinforcementDocumento4 pagineReinforcementKainaat YaseenNessuna valutazione finora
- Barlow, D., Durand, M. Hofmann, S. (2018) - Abnormal Psychology An Integrative Approach. Boston CENGAGE Learning. Capítulo 3.Documento30 pagineBarlow, D., Durand, M. Hofmann, S. (2018) - Abnormal Psychology An Integrative Approach. Boston CENGAGE Learning. Capítulo 3.PARRA LUGO SANDRA MANUELANessuna valutazione finora
- Jurnal No 3 (Learning Cycle 5E)Documento7 pagineJurnal No 3 (Learning Cycle 5E)Alma SiwiNessuna valutazione finora
- Activity and Assessment 4 5Documento20 pagineActivity and Assessment 4 5Josephine FernandezNessuna valutazione finora
- International Journal of Nursing Studies: Thomas A. Lang, Douglas G. AltmanDocumento5 pagineInternational Journal of Nursing Studies: Thomas A. Lang, Douglas G. AltmanNepjune RxNessuna valutazione finora
- JPNR - Regular Issue 03 - 357 PDFDocumento8 pagineJPNR - Regular Issue 03 - 357 PDFAyesha NaeemNessuna valutazione finora
- Competence Assessment and Verification Guidelines PDFDocumento21 pagineCompetence Assessment and Verification Guidelines PDFSachin SahooNessuna valutazione finora