Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Project
Caricato da
RauhweltDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Project
Caricato da
RauhweltCopyright:
Formati disponibili
1. Why insect can freely run along the surface of a quiet pond. ?
It's tiny mass and the geometry of its legs allow it to be supported by the high
2. If carefully placed on the surface,Why a small needle can be made to float on the surface of water even though it is several times as dense as water. ? If the surface is agitated to break up the surface tension, then needle will quickly sink
3. Why will water rise higher in a smaller tube ? Capillary action is the result of adhesion and surface tension. Adhesion of water to the walls of a vessel will cause an upward force on the liquid at the edges and result in a meniscus which turns upward. The surface tension acts to hold the surface intact, so instead of just the edges moving upward, the whole liquid surface is dragged upward.
4. Why the shape of liquid droplets. Although easily deformed, droplets of water tend to be pulled into a spherical shape
5. Why it dropped a short time later, and took a more nearly spherical shape as it fell ?
The relatively high surface tension of water accounts for the ease with which it can be nebulized, or placed into aerosol form. Low surface tension liquids tend to evaporate quickly and are difficult to keep in an aerosol form.
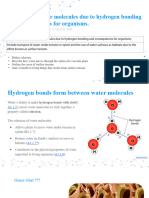
The cohesive forces between molecules down into a liquid are shared with all neighboring atoms. Those on the surface have no neighboring atoms above, and exhibit stronger attractive forces upon their nearest neighbors on the surface. This enhancement of the intermolecular attractive forces at the surface is called surface tension. Molecules liquid state experience strong intermolecular attractive forces. When those forces are between like molecules, they are referred to as cohesive forces. For example, the molecules of a water droplet are held together by cohesive forces, and the especially strong cohesive forces at the surface constitute surface tension. When the attractive forces are between unlike molecules, they are said to be adhesive forces. The adhesive forces between water molecules and the walls of a glass tube are stronger than the cohesive forces lead to an upward turning meniscus at the walls of the vessel and contribute to capillary action. The attractive forces between molecules in a liquid can be viewed as residual electrostatic forces and are sometimes called van der Waals forces or van der Waals bonds.
If need you can do smaller tube water rising.
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Gse Solution9Documento3 pagineGse Solution9Nayan PaulNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem LiquidsDocumento2 pagineChem LiquidsHannah Rae S. RuizolNessuna valutazione finora
- CHEM - Surface TensionDocumento2 pagineCHEM - Surface TensionReyster LalimNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Tension - Chemistry LibreTextsDocumento3 pagineSurface Tension - Chemistry LibreTextsmuthamizh rajuNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface TensionDocumento2 pagineSurface TensionShashank ChheniyaNessuna valutazione finora
- Ministry of Higher Education & Scientific Research Misan University Engineering College Petroleum DepartmentDocumento11 pagineMinistry of Higher Education & Scientific Research Misan University Engineering College Petroleum DepartmentMohammad MakeyNessuna valutazione finora
- Cohesive and Adhesive ForcesDocumento3 pagineCohesive and Adhesive ForcesAhmad RaihanNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscosity and Surface TensionDocumento15 pagineViscosity and Surface TensionAtul KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics Prelim 2Documento4 pagineFluid Mechanics Prelim 2Santa mariaNessuna valutazione finora
- Floating Needle-WPS OfficeDocumento2 pagineFloating Needle-WPS OfficeAnnie Valenzona CablasNessuna valutazione finora
- UntitledDocumento3 pagineUntitledKate Loren BacarroNessuna valutazione finora
- F KS3 Walking Water WorksheetDocumento8 pagineF KS3 Walking Water Worksheetชาเย็น เย็นชาNessuna valutazione finora
- Chemistry Properties of WaterDocumento14 pagineChemistry Properties of WaterKate PerojaNessuna valutazione finora
- REPORT SHEET Properties and Purification of Water PDFDocumento12 pagineREPORT SHEET Properties and Purification of Water PDFAbegail CantonesNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface TensionDocumento15 pagineSurface TensionAnurup ChattopadhyayNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface TensionDocumento2 pagineSurface TensionBizay MarikhuNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Liquids-Lesson3Documento25 pagineProperties of Liquids-Lesson3Jazzy OcuamanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson3 - Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDocumento16 pagineLesson3 - Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesLemonadeNessuna valutazione finora
- Brownian Motion and DiffusionDocumento4 pagineBrownian Motion and DiffusionANam MUkri100% (3)
- Phy 105 - 4 Solids-ADocumento6 paginePhy 105 - 4 Solids-AalakaolamuhammadNessuna valutazione finora
- The Physics of Superheroes: Spectacular Second Edition: Fresh Air UnderwaterDocumento4 pagineThe Physics of Superheroes: Spectacular Second Edition: Fresh Air UnderwaterSureshSwaminathanNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson: Distribution of Water On EarthDocumento5 pagineLesson: Distribution of Water On EarthB15 Salomon, IoanNessuna valutazione finora
- 5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Documento23 pagine5 Impending Signs of Landslides and Sinkholes Continuation... Feb. 8 2021Shiela Jean H. RescoNessuna valutazione finora
- Computer Systems Institute: Senior High School DepartmentDocumento9 pagineComputer Systems Institute: Senior High School DepartmentMaureen Zubeldia MendioroNessuna valutazione finora
- Properties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesDocumento20 pagineProperties of Liquids and Intermolecular ForcesTiburcio JayzelNessuna valutazione finora
- 03 Module 2 Lesson 1 Physical Properties of WaterDocumento13 pagine03 Module 2 Lesson 1 Physical Properties of WaterBruce GreenNessuna valutazione finora
- Viscosity and Surface TensionDocumento2 pagineViscosity and Surface TensionMichael HeryantoNessuna valutazione finora
- FluidDocumento3 pagineFluidreannNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 2Documento61 pagineChem 2jvmijaresNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface TensionDocumento28 pagineSurface TensionNur Sofia0% (2)
- Surface Tension and Water: Cohesive ForcesDocumento2 pagineSurface Tension and Water: Cohesive ForcesLydia AjengNessuna valutazione finora
- Mini Proyect The E.CDocumento2 pagineMini Proyect The E.CLUIS ROJAS SANTANANessuna valutazione finora
- IntroductionDocumento6 pagineIntroductionleoyong509Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Kinematics in Submerged Bodies: FLUID KINEMATICSDa EverandFluid Kinematics in Submerged Bodies: FLUID KINEMATICSNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Intermolecular ForcesDocumento7 pagineTypes of Intermolecular ForcesRhenczell Angela VelascoNessuna valutazione finora
- ViscosityDocumento4 pagineViscosityBabatunde Victor JuniorNessuna valutazione finora
- Water Conference HandoutDocumento11 pagineWater Conference HandoutRichard AwNessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Tension: Practical General ChemistryDocumento4 pagineSurface Tension: Practical General Chemistryعمر الرفاعيNessuna valutazione finora
- Break The Tension A Water ExperimentDocumento3 pagineBreak The Tension A Water ExperimentDeyann ZoldyckNessuna valutazione finora
- A1.1.3 Cohesion of Water Molecules Due To Hydrogen Bonding and Consequences For OrganismsDocumento15 pagineA1.1.3 Cohesion of Water Molecules Due To Hydrogen Bonding and Consequences For Organismstaiga.aisaka14404Nessuna valutazione finora
- Surface TensionDocumento7 pagineSurface TensionMohd. ArhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Scientific Writing Excerpt - Capillary Attraction or Attraction of CohesionDocumento6 pagineScientific Writing Excerpt - Capillary Attraction or Attraction of Cohesion0022662Nessuna valutazione finora
- Bio 112 - Activity 4Documento3 pagineBio 112 - Activity 4LAGMAY, Daniel Scott G.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Dye Penetrant Testing Q&ADocumento5 pagineDye Penetrant Testing Q&AHarry FrankNessuna valutazione finora
- Water RLW AsgnDocumento2 pagineWater RLW AsgnTomáš Tommy NagyNessuna valutazione finora
- Siagan, Karl Gerard M. (Activity #1 IMF's)Documento5 pagineSiagan, Karl Gerard M. (Activity #1 IMF's)Karl SiaganNessuna valutazione finora
- ACTIVITYFORPHYSCIDocumento4 pagineACTIVITYFORPHYSCIThalia Diosenne ArabesNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem 02 - Mod - WK1L2Documento2 pagineChem 02 - Mod - WK1L22082862Nessuna valutazione finora
- Fluid Mechanics (Output)Documento11 pagineFluid Mechanics (Output)Gel CabansagNessuna valutazione finora
- Toddle - (A1 2Documento44 pagineToddle - (A1 2Youssef SamehNessuna valutazione finora
- Science Involved in Floating Paper Clip Science Experiment GuidelinesDocumento4 pagineScience Involved in Floating Paper Clip Science Experiment GuidelinesSHIELA RUBIONessuna valutazione finora
- Untitled PresentationDocumento13 pagineUntitled PresentationKristalyn CabreraNessuna valutazione finora
- Identify Root Hair Cells, As Seen Under The Light Microscope, and Describe Their FunctionsDocumento16 pagineIdentify Root Hair Cells, As Seen Under The Light Microscope, and Describe Their FunctionsMandla RebirthNessuna valutazione finora
- Trees & Capillary Action: Home ProgramsDocumento25 pagineTrees & Capillary Action: Home ProgramsRiddhi KatheNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem Alipongga'sDocumento1 paginaChem Alipongga'sJames Ramcel AliponggaNessuna valutazione finora
- ParlamentoDocumento1 paginaParlamentoMARIA ALEXANDRA POLONessuna valutazione finora
- Fluids at Rest and in MotionDocumento8 pagineFluids at Rest and in MotionSoala WaribokoNessuna valutazione finora
- Colloid, Emulsion, Mixture Worksheet0Documento82 pagineColloid, Emulsion, Mixture Worksheet0sayedrezha1Nessuna valutazione finora
- CH 21.2 The Vascular System EditedDocumento29 pagineCH 21.2 The Vascular System Editedo45tjit4Nessuna valutazione finora
- Surface Tension: Capillary PressureDocumento5 pagineSurface Tension: Capillary PressureDorn AdamsNessuna valutazione finora
- Fire CodeDocumento1 paginaFire CodeShainette VillarazaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pinoy Ree - EeDocumento138 paginePinoy Ree - EeChilvin ChipmunkNessuna valutazione finora
- Micromechanical Testing of Thin Die: (Nordson DAGE UK)Documento2 pagineMicromechanical Testing of Thin Die: (Nordson DAGE UK)Thanalachmy GopiNessuna valutazione finora
- Plumbing Design Calculation - North - Molino - PH1 - 5jun2017Documento5 paginePlumbing Design Calculation - North - Molino - PH1 - 5jun2017Jazent Anthony RamosNessuna valutazione finora
- IJARIE Paper 17936 PDFDocumento7 pagineIJARIE Paper 17936 PDFArbelyn RoblesNessuna valutazione finora
- Lesson 2.1 Earth As The Only Habitable PlanetDocumento37 pagineLesson 2.1 Earth As The Only Habitable Planetrosie sialanaNessuna valutazione finora
- EMI Course CatalogDocumento645 pagineEMI Course CatalogFarouk OthmaniNessuna valutazione finora
- The Prosecution of Kim Jong Il - Accountability in A Post 9-11 WorldDocumento21 pagineThe Prosecution of Kim Jong Il - Accountability in A Post 9-11 WorldimpunitywatchNessuna valutazione finora
- NEWS BD RAE Letter of Intent-Press-release1Documento2 pagineNEWS BD RAE Letter of Intent-Press-release1Anthony D.Nessuna valutazione finora
- Brosura Oxyhelp PDFDocumento12 pagineBrosura Oxyhelp PDFAftab Naseem100% (1)
- Assignment 4Documento4 pagineAssignment 4ShabihNessuna valutazione finora
- CSA11 CholelithiasisDocumento3 pagineCSA11 CholelithiasisBerlon LacsonNessuna valutazione finora
- BS Pharmacy - ProspectusDocumento9 pagineBS Pharmacy - ProspectusDomz BucadNessuna valutazione finora
- Nato Code Numbers: Scope of ListDocumento6 pagineNato Code Numbers: Scope of ListRain HeinNessuna valutazione finora
- TOCDocumento14 pagineTOCAthirah HattaNessuna valutazione finora
- Matter and Change 2008 Chapter 14Documento40 pagineMatter and Change 2008 Chapter 14cattmy100% (1)
- Abrams Clinical Drug Therapy Rationales For Nursing Practice 11th Edition Test BankDocumento6 pagineAbrams Clinical Drug Therapy Rationales For Nursing Practice 11th Edition Test BankWilliam Nakken100% (28)
- ES9-62 Ingestive Cleaning PDocumento9 pagineES9-62 Ingestive Cleaning PIfran Sierra100% (1)
- ISBB CompilationDocumento6 pagineISBB CompilationElla SalesNessuna valutazione finora
- Ans Sheet Chemical 23111Documento96 pagineAns Sheet Chemical 23111Aejaz MujawarNessuna valutazione finora
- Lab Risk AssessmentDocumento8 pagineLab Risk Assessmentaqilah haronNessuna valutazione finora
- Turbo Lab 1Documento10 pagineTurbo Lab 1Seng SoonNessuna valutazione finora
- Mary Kay FinalDocumento17 pagineMary Kay Finalharsh0695Nessuna valutazione finora
- Mammalian Temperature Regulation - 12Documento13 pagineMammalian Temperature Regulation - 12wadson chirwaNessuna valutazione finora
- Timbers Lesson 2Documento18 pagineTimbers Lesson 2bright possibleNessuna valutazione finora
- SwivelDocumento29 pagineSwivelluisedonossaNessuna valutazione finora
- TableBookErrata PDFDocumento4 pagineTableBookErrata PDFIbnuyusoff77Nessuna valutazione finora
- Ocean StarDocumento36 pagineOcean Starrobertshepard1967Nessuna valutazione finora
- Kristen Swanson's Theory of CaringDocumento12 pagineKristen Swanson's Theory of CaringAlexandria David50% (2)
- Report of Initial / Annual / Intermediate / Renewal / General Examination SurveyDocumento9 pagineReport of Initial / Annual / Intermediate / Renewal / General Examination SurveyJagjit SinghNessuna valutazione finora