Documenti di Didattica
Documenti di Professioni
Documenti di Cultura
Polymer and Natural Rubber
Caricato da
Lyn Xi LauDescrizione originale:
Copyright
Formati disponibili
Condividi questo documento
Condividi o incorpora il documento
Hai trovato utile questo documento?
Questo contenuto è inappropriato?
Segnala questo documentoCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Polymer and Natural Rubber
Caricato da
Lyn Xi LauCopyright:
Formati disponibili
Only 4 types of monomers, but if we look at the human species only, how many different individuals are there?
Two main types
Natural
Synthetic
Also can be classified as
Condensation polymers
Addition polymers
Depends on how the polymers are formed Structural formula of monomer is not the same as structural formula of repeating unit
C6H12O6
(C6H10O5)
C5H8 Same molecular formula
poly
(C5H8 )n
-No loss of atoms/ molecules during polymerization
Synthetic polymers / plastic Animation
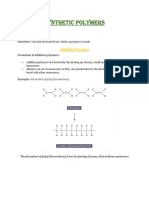
Polyethene/ polyethylene is an addition polymer.
In the presence of a catalyst, ethene molecules add to each other to form the polymer, with no loss of atoms/ molecules. The double bond breaks and 2 new single bonds form, connecting to other ethene molecules
Elasticity Oxidation
Ordinary conditions
Effect of heat
C=C makes natural rubber prone to oxidation Loss of elasticity Prevented by adding carbon or antioxidants Low T hard, brittle High T soft and sticky
Stretched polymer chains straighten
Effect of solvent
oils
Waterproof But soluble in hydrocarbons benzene, petrol, lubricating
Strain removed
Use the graphic cue to come up with a story explaining the picture At the end of this activity, each group rep will tell the story they created, starting with Group 1 (picture #1)
C=C
S2Cl2 , methylbenzene
Preparing vulcanized rubber
Heat latex with sulphur at ~140C, catalyst: ZnO
Disulphide linkages, -S-S- : - Stronger - more elastic - Higher melting point, does not become soft and sticky - More resistant to oxidation
S2Cl2 , methylbenzene
Soak latex with in a solution of disulphur dichloride in methylbenzene
Potrebbero piacerti anche
- Polymers CH 101 (Updated Version) FALL 22Documento50 paginePolymers CH 101 (Updated Version) FALL 22Haider AliNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers: Hermann StaudingerDocumento5 paginePolymers: Hermann Staudingermohsin160Nessuna valutazione finora
- Chp. 11 Notes: 11.1 PetroleumDocumento4 pagineChp. 11 Notes: 11.1 PetroleumRuheen KumarNessuna valutazione finora
- PolymerisationDocumento36 paginePolymerisationMustafa MuazNessuna valutazione finora
- Petrochemicals and PolymersDocumento22 paginePetrochemicals and PolymersSumedha ZopeNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers: Hermann StaudingerDocumento37 paginePolymers: Hermann StaudingerGirijaKaushikNessuna valutazione finora
- Types of Polymers: Molecular Weight Crystallinity CrosslinkingDocumento13 pagineTypes of Polymers: Molecular Weight Crystallinity CrosslinkingspallocNessuna valutazione finora
- PolymersDocumento7 paginePolymersrayman9Nessuna valutazione finora
- What Is A Polymer?: MonomersDocumento44 pagineWhat Is A Polymer?: MonomersMahe MahendranNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethylene ProductionDocumento34 pagineEthylene ProductionWesleyNessuna valutazione finora
- Basics of PolymerDocumento28 pagineBasics of PolymervishwanathanskNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Industry-Set-4Documento17 paginePolymer Industry-Set-4qamaralmahseriNessuna valutazione finora
- POLYMERISATIONqDocumento6 paginePOLYMERISATIONqjpkaomeNessuna valutazione finora
- Methanol DataDocumento29 pagineMethanol DataSantosh Kumar NathNessuna valutazione finora
- PolimerDocumento22 paginePolimerDhea Kana ZhafiraNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter Polymerisation MethodDocumento56 pagineChapter Polymerisation MethodwaniNessuna valutazione finora
- Chapter 4: Carbon Compounds: Carbon Mineral Carbonates, Natural Gas, Oil and Coal. Graphite Diamond. Allotrophy GraphiteDocumento15 pagineChapter 4: Carbon Compounds: Carbon Mineral Carbonates, Natural Gas, Oil and Coal. Graphite Diamond. Allotrophy GraphiteLemathaNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymeric Materials - Part IIDocumento49 paginePolymeric Materials - Part IIRidhwan HaliqNessuna valutazione finora
- HSC Production of Materials. BestnotesDocumento24 pagineHSC Production of Materials. Bestnotes16choi.michaelNessuna valutazione finora
- Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 14: Organic ChemistryDocumento4 pagineCambridge IGCSE Chemistry Topic 14: Organic ChemistryPixel -StormNessuna valutazione finora
- Unit-1 Introduction To PolymersDocumento40 pagineUnit-1 Introduction To Polymerssantosh chikkamathNessuna valutazione finora
- Lecture - Engineeirng Materilas - Week 45678Documento51 pagineLecture - Engineeirng Materilas - Week 45678Salar KhanNessuna valutazione finora
- Denture Base Materials 12Documento70 pagineDenture Base Materials 12Rohith GanigaNessuna valutazione finora
- PolymersDocumento33 paginePolymersNithishNessuna valutazione finora
- Cap 1 2019-10-27 08 - 57 - 04Documento18 pagineCap 1 2019-10-27 08 - 57 - 04Esteban CorderoNessuna valutazione finora
- Chem5 ProductionMaterialsUDocumento39 pagineChem5 ProductionMaterialsUKevin Huang100% (2)
- In This Modern World, Polymers Are An Integral Part of Every One's Life Style. They HaveDocumento13 pagineIn This Modern World, Polymers Are An Integral Part of Every One's Life Style. They HaveMohamed AashiqNessuna valutazione finora
- PolymersDocumento17 paginePolymersleaf5Nessuna valutazione finora
- Polymeric mater-WPS OfficeDocumento3 paginePolymeric mater-WPS OfficeNina Riana HarahapNessuna valutazione finora
- Separation of Polymers by Solvent FractionationDocumento6 pagineSeparation of Polymers by Solvent FractionationSzePT100% (2)
- Reisins in ConservationDocumento5 pagineReisins in ConservationIngrid GeorgescuNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers IntroductionDocumento28 paginePolymers Introductionleela777Nessuna valutazione finora
- Organic Materials: Prepared By: Lecturer IOE, Pashchimanchal CampusDocumento26 pagineOrganic Materials: Prepared By: Lecturer IOE, Pashchimanchal CampusbijenNessuna valutazione finora
- 1 PolymerDocumento55 pagine1 Polymerbt21102047 Vishwajeet YadavNessuna valutazione finora
- CL 304 - CPT Ethylene and Propylene PolymerizationDocumento23 pagineCL 304 - CPT Ethylene and Propylene PolymerizationRelaxation MasterNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer Science and Technology 2Documento93 paginePolymer Science and Technology 2xnzrjp55tsNessuna valutazione finora
- SCY1616Documento50 pagineSCY1616MohsinAliNessuna valutazione finora
- Preliminary Chemistry Notes NSWDocumento56 paginePreliminary Chemistry Notes NSWfocuc980% (1)
- Industrial PolymersDocumento63 pagineIndustrial PolymerssoumyajyotideyNessuna valutazione finora
- Synthetic PolymersDocumento7 pagineSynthetic PolymersHalal BoiNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymer FinalDocumento38 paginePolymer Finalإحسان خالد جودة الشحات ٣٥٧٣Nessuna valutazione finora
- States of Order in PolymersDocumento28 pagineStates of Order in PolymersMianHusnain IqbalNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers NotesDocumento10 paginePolymers NotesThaarvena RetinaNessuna valutazione finora
- L-3 Mee 241Documento37 pagineL-3 Mee 241Promee Nafiza AnjumNessuna valutazione finora
- Production of Methanol From Natural GasDocumento219 pagineProduction of Methanol From Natural GasIsmail100% (4)
- General Chemistry I.las 6Documento5 pagineGeneral Chemistry I.las 6bmiquinegabrielNessuna valutazione finora
- Introduction To Polymer and BiopolymerDocumento73 pagineIntroduction To Polymer and Biopolymersyafiq zulkefliNessuna valutazione finora
- Plastic Polymers CompleteDocumento57 paginePlastic Polymers CompleteMaria Ozao100% (1)
- Methanol ProjectDocumento50 pagineMethanol Projectyesuvaraprasad100% (5)
- 27 Polymer Revision Notes Getmarks AppDocumento24 pagine27 Polymer Revision Notes Getmarks AppYashitaNessuna valutazione finora
- PolimerDocumento31 paginePolimerAlief MoulanaNessuna valutazione finora
- By-Pramesh SharmaDocumento39 pagineBy-Pramesh SharmaAashish SapkotaNessuna valutazione finora
- Pom ChemDocumento15 paginePom ChemalbiNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers Chemeng Lec QuizzesDocumento27 paginePolymers Chemeng Lec QuizzesTonyTony ChopperNessuna valutazione finora
- Polymers OEDocumento36 paginePolymers OEBikash MahasethNessuna valutazione finora
- Presentation For SaifulDocumento13 paginePresentation For SaifulBoier Sesh PataNessuna valutazione finora
- PolymerisationDocumento59 paginePolymerisationkid unique100% (2)
- Material Prepared By: Chemistry Faculty Page 1 of 33Documento33 pagineMaterial Prepared By: Chemistry Faculty Page 1 of 33Abinav NarayananNessuna valutazione finora
- 2011 Chemistry NotesDocumento70 pagine2011 Chemistry NotesAbdullionNessuna valutazione finora
- Ethanol Fuel: Learn to Make and Use Ethanol to Power Your VehiclesDa EverandEthanol Fuel: Learn to Make and Use Ethanol to Power Your VehiclesNessuna valutazione finora
- CBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science SA2 Set 7Documento13 pagineCBSE Sample Paper Class 9 Science SA2 Set 7PALAK SHARMANessuna valutazione finora
- 2022 Specimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme 1Documento4 pagine2022 Specimen Paper 1 Mark Scheme 1Herman HermanNessuna valutazione finora
- Astm D6321-98-2004Documento3 pagineAstm D6321-98-2004Thyagu LingamurthyNessuna valutazione finora
- Practice Test 1 + 2Documento19 paginePractice Test 1 + 2yếnNessuna valutazione finora
- The Meal Must Go On-Student VersionDocumento4 pagineThe Meal Must Go On-Student VersionSheena ViloriaNessuna valutazione finora
- List BRG TGL 12Documento49 pagineList BRG TGL 12Rizal MuhammarNessuna valutazione finora
- Op Amp AssignmentDocumento10 pagineOp Amp AssignmentJuan-Wian CoetzerNessuna valutazione finora
- CH 7. Pneumatic and HydroulicDocumento20 pagineCH 7. Pneumatic and HydroulicAbenezer Tasew100% (1)
- Rewoquat We 45 TDS 12 02 01Documento3 pagineRewoquat We 45 TDS 12 02 01chintanictNessuna valutazione finora
- Heavy Earth Moving MachinaryDocumento34 pagineHeavy Earth Moving MachinaryMAZHAR ALAMNessuna valutazione finora
- Bergeron Et Al 2023 Use of Invasive Brain Computer Interfaces in Pediatric Neurosurgery Technical and EthicalDocumento16 pagineBergeron Et Al 2023 Use of Invasive Brain Computer Interfaces in Pediatric Neurosurgery Technical and EthicalPriscilla MelindaNessuna valutazione finora
- Daitoumaru and Panstar GenieDocumento41 pagineDaitoumaru and Panstar GeniePedroNessuna valutazione finora
- JC 1010Documento19 pagineJC 1010mcsmiley11Nessuna valutazione finora
- Literature ReviewDocumento3 pagineLiterature ReviewAina Reyes100% (1)
- Project Risk Management in Hydropower Plant Projects A Case Study From The State-Owned Electricity Company of IndonesiaDocumento16 pagineProject Risk Management in Hydropower Plant Projects A Case Study From The State-Owned Electricity Company of IndonesiaJoli SmithNessuna valutazione finora
- Research Article: International Research Journal of PharmacyDocumento5 pagineResearch Article: International Research Journal of PharmacyAlfrets Marade SianiparNessuna valutazione finora
- Learn Mandarin Chinese: Most Popular Chinese Tales With AnimalsDocumento65 pagineLearn Mandarin Chinese: Most Popular Chinese Tales With AnimalseChineseLearning100% (6)
- 02-779 Requirements For 90-10 Copper - Nickel - Alloy Part-3 TubingDocumento47 pagine02-779 Requirements For 90-10 Copper - Nickel - Alloy Part-3 TubingHattar MNessuna valutazione finora
- Sea Shanty PrintDocumento3 pagineSea Shanty PrintDiego DracvsNessuna valutazione finora
- Kantha Embroidery by Nanduri Asha, Shreya Gulati, Saloni PriyaDocumento17 pagineKantha Embroidery by Nanduri Asha, Shreya Gulati, Saloni PriyaShreyaa Gulati100% (3)
- April262019 Airline Economic Analysis 2018-2019vfwebDocumento62 pagineApril262019 Airline Economic Analysis 2018-2019vfwebapi-548139140Nessuna valutazione finora
- DVH-P4950 P4050Documento111 pagineDVH-P4950 P4050roto44100% (1)
- Animal Cells PDFDocumento4 pagineAnimal Cells PDFFalah HabibNessuna valutazione finora
- My 6-Step Plan For Diagnosing & Managing The Pruritic DogDocumento6 pagineMy 6-Step Plan For Diagnosing & Managing The Pruritic DogAnonymous TDI8qdYNessuna valutazione finora
- A Review On Battery Management System For Electric VehiclesDocumento6 pagineA Review On Battery Management System For Electric Vehiclesomkar chitnisNessuna valutazione finora
- Exam Materials ScienceDocumento10 pagineExam Materials ScienceChimzoe CatalanNessuna valutazione finora
- Module 1 - AE4 - Review of Basic Mathematical Concepts (For Discussion)Documento36 pagineModule 1 - AE4 - Review of Basic Mathematical Concepts (For Discussion)Kimberly Jean LautrizoNessuna valutazione finora
- Aeration PaperDocumento11 pagineAeration PapersehonoNessuna valutazione finora
- Raw Material Chemical AnalysisDocumento41 pagineRaw Material Chemical AnalysisVinod Kumar VermaNessuna valutazione finora
- LEC - 19 - Task of Bitcoin MinersDocumento36 pagineLEC - 19 - Task of Bitcoin MinersKarunesh AnandNessuna valutazione finora